
A List of Earth Observation Satellites & Optical Parameters
One of the key tools for monitoring changes occurring on the Earth's surface are observation satellites. Satellite observations enable the acquisition of imagery used in Earth sciences, agriculture, forestry, and crisis management. Modern optical satellites offer a wide range of spatial, spectral, and temporal resolutions, allowing for precise analyses of various phenomena occurring on the Earth's surface.
Optical Imaging Parameters
To fully understand the specifications of individual satellites, we should familiarize ourselves with their key technical parameters, which significantly impact the quality and application of satellite data.
Spatial Resolution – This parameter defines the smallest object that can be identified in a satellite image. The lower the value (e.g., 0.5 m), the higher the image quality and the greater the level of detail.
Spectral Bands – Each satellite captures images in different wavelength ranges, such as visible light (R – red, G – green, B – blue), near-infrared (NIR), or shortwave infrared (SWIR). The number and range of bands influence the ability to analyze surface features.
Revisit Time – This defines how frequently a satellite passes over a given area and captures new images. A shorter revisit time enhances the ability to monitor dynamic changes on the Earth's surface.
Applications of Satellite Data
Satellite data is utilized across a wide range of fields. Some of the primary applications of satellite imagery include:
Monitoring climate change
Land cover analysis and urbanization tracking
Natural resource management
Crisis management and disaster response
Precision agriculture and crop monitoring
Forestry and ecosystem management
Urban planning and city development
Military surveillance and geopolitical intelligence
Modern analytical platforms, such as OnGeo Intelligence, leverage satellite imagery for precise analysis of urban areas, detection of land cover changes, and support for public institutions and companies involved in spatial analysis. These data can be particularly useful in legal dispute resolution, assessing the legitimacy of compensation claims, and monitoring changes near specific properties.
Each satellite has unique imaging parameters that make it more suitable for specific applications. Below, we present detailed information on the most important optical satellites along with their practical applications.
Overview of Key Earth Observation Satellites
Landsat 8 (NASA/USGS)
Manufacturer: NASA, USGS
Resolution: 15 m (panchromatic), 30 m (multispectral)
Spectral Bands: 11 bands (visible, near-infrared, mid-infrared, thermal)
Revisit Time: 16 days
Applications:
Long-term monitoring of land cover changes, such as deforestation and urbanization.
Observation of surface water quality and human impact on aquatic ecosystems.
Climate change analysis, including the effects of drought and temperature variations on agriculture.
Sentinel-2A/B (ESA)
Manufacturer: Airbus for ESA
Resolution: 10 m (visible), 20 m (near-infrared)
Spectral Bands: 13 bands
Revisit Time: 10 days (each satellite), 5 days in a two-satellite system
Applications:
Precision agriculture – assessing crop health, soil moisture, and chlorophyll levels.
Monitoring forests and deforestation to evaluate ecosystem changes.
Analysis of atmospheric pollution and the impact of airborne particles on the environment.
WorldView-3 (Maxar Technologies)
Manufacturer: Maxar Technologies (DigitalGlobe)
Resolution: 0.31 m (panchromatic), 1.24 m (multispectral)
Spectral Bands: 16 bands, including SWIR (shortwave infrared)
Revisit Time: 5 days
Applications:
Urban area analysis and infrastructure monitoring.
Support for military operations and strategic reconnaissance.
Detection of thermal anomalies, such as gas leaks or wildfires.
Pléiades 1A/1B (Airbus)
Manufacturer: Airbus
Resolution: 0.5 m (panchromatic), 2 m (multispectral)
Spectral Bands: 4 bands (B, G, R, NIR)
Revisit Time: 26 days
Applications:
Urban planning and land development analysis.
Support for humanitarian missions by monitoring natural disaster impacts.
Detailed analysis of building structures and civil engineering projects.
SkySat (Planet)
Manufacturer: Planet Labs
Resolution: 0.5 m (panchromatic), 2 m (multispectral)
Spectral Bands: 4 bands (B, G, R, NIR)
Revisit Time: <1 day (satellite constellation)
Applications:
Real-time monitoring of industrial and commercial activity.
Support for precision agriculture by analyzing plant growth.
Observation of environmental changes, such as glacier retreat.
GeoEye-1 (Maxar Technologies)
Manufacturer: Maxar Technologies (DigitalGlobe)
Resolution: 0.46 m (panchromatic), 1.84 m (multispectral)
Spectral Bands: 4 bands (B, G, R, NIR)
Revisit Time: 3 days
Applications:
Monitoring urban and transportation infrastructure changes.
Observing agricultural areas and crop management.
Surveillance of strategic sites and military applications.
SuperView-1 (Beijing Space View Technology)
Manufacturer: Beijing Space View Technology
Resolution: 0.5 m (panchromatic), 2 m (multispectral)
Spectral Bands: 4 bands (B, G, R, NIR)
Revisit Time: 2 days
Applications:
Structural analysis of buildings and engineering constructions.
Support for archaeological and geodetic research.
High-precision land change inventory.
Kompsat-3A (KARI - Korea Aerospace Research Institute)
Manufacturer: Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI)
Resolution: 0.55 m (panchromatic), 2.2 m (multispectral)
Spectral Bands: 4 bands (B, G, R, NIR)
Revisit Time: 28 days
Applications:
Monitoring natural resources and land cover changes.
Observing disaster impacts and crisis management.
Military and intelligence applications.
TripleSat-1-3 (SSTL - Surrey Satellite Technology)
Manufacturer: Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd. (SSTL)
Resolution: 0.8 m (panchromatic), 3.2 m (multispectral)
Spectral Bands: 4 bands (B, G, R, NIR)
Revisit Time: 1 day (constellation-based)
Applications:
Fast and precise real-time imaging.
Monitoring environmental and urban changes.
Intelligence and military applications.
SPOT 6 & 7 (Airbus)
Manufacturer: Airbus Defence and Space
Resolution: 1.5 m (panchromatic), 6 m (multispectral)
Spectral Bands: 4 bands (B, G, R, NIR)
Revisit Time: 26 days
Applications:
Monitoring land use changes and urban planning.
Managing natural resources and agricultural monitoring.
Supporting emergency services in disaster-stricken areas.
Pléiades Neo (Airbus)
Manufacturer: Airbus Defence and Space
Resolution: 0.3 m (panchromatic), 1.2 m (multispectral)
Spectral Bands: 4 bands (B, G, R, NIR)
Revisit Time: 1 day
Applications:
High-precision mapping of cities and infrastructure.
Environmental monitoring and land cover analysis.
Intelligence surveillance of strategic locations.
Jilin-1 Optical (Chang Guang Satellite Technology)
Manufacturer: Chang Guang Satellite Technology
Resolution: 0.72 m (panchromatic), 2.88 m (multispectral)
Spectral Bands: 4 bands (B, G, R, NIR)
Revisit Time: 3.3 days
Applications:
Rapid monitoring of infrastructure and agricultural changes.
Tracking environmental changes and natural disasters.
Urban area observation and city development control.
WorldView-4 (Maxar Technologies)
Manufacturer: Maxar Technologies (DigitalGlobe)
Resolution: 0.31 m (panchromatic), 1.24 m (multispectral)
Spectral Bands: 4 bands (B, G, R, NIR)
Revisit Time: 1 day
Applications:
Highly detailed geodetic and cartographic analyses.
Support for military operations and reconnaissance missions.
Precise 3D modeling of cities and infrastructure objects.
This overview highlights the diverse capabilities and applications of key Earth observation satellites, showcasing their role in environmental monitoring, urban planning, disaster management, and strategic intelligence.
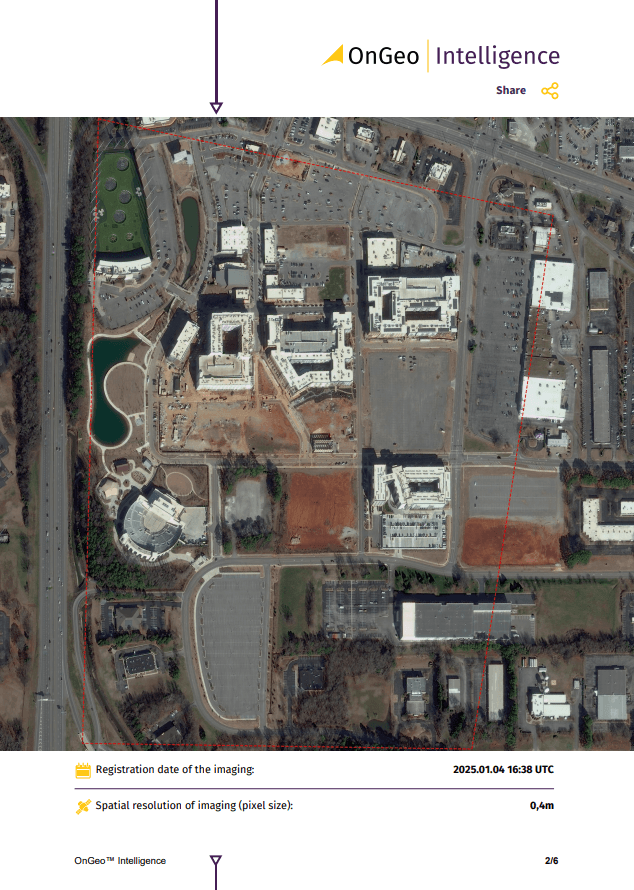
The power of OnGeo-Intelligence’s Satellite Image Report
- No signup needed: There is no long-term contract to subscribe. Just buy a report when you need it.
- High and Very High-Resolution imagery: Get high and very high-resolution satellite imagery right on the shelf to fit your specific needs. We are sure you will find we exceed your expectations.
- Layman’s language in PDF: The report is in PDF format, so anyone can read it and understand it.
- Instant, fast: The good thing about the report is you will not have to wait longer to buy. You will have it instantly.
- Global: Location doesn’t matter in this case because you can get an image of any place in this world.
Conclusion
Optical satellites form the foundation of modern Earth observation systems, providing essential data for making critical decisions across various fields. In the future, advancements in satellite technology will enable even more precise monitoring of our planet.
With a wide range of available satellites, from large scientific missions to commercial constellations delivering real-time imagery, the applications of remote sensing data continue to expand, driving progress in science, economy, and technology. Modern analytical tools, such as OnGeo Intelligence, facilitate the efficient processing and interpretation of satellite imagery, supporting key decision-making in environmental protection, urban planning, and landscape change monitoring.