What is temporal resolution in satellite remote sensing?
Temporal resolution refers to how frequently a satellite revisits and images the same area. This frequency, known as the "revisit rate", is expressed in days or hours, depending on the satellite system.
- High temporal resolution means a satellite revisits a location frequently, sometimes daily or multiple times per day.
- Low temporal resolution indicates longer intervals between revisits, often weeks or months.
This metric is crucial for timely and consistent data acquisition, empowering scientists, analysts, and decision-makers to track changes as they unfold and take prompt action.
How temporal resolution works: a closer look
Several factors influence a satellite's temporal resolution, including orbit type, sensor capabilities, and swath width (the ground area imaged in a single pass).
- Polar-orbiting satellites like NASA's Terra and Aqua MODIS revisit areas every 1–2 days, offering global coverage.
- Satellites with narrower swath widths, such as Landsat 8, revisit areas every 16 days, providing detailed observations.
- Geostationary satellites maintain a fixed position over one area, enabling continuous observation but with less spatial detail.
Modern Earth Observation systems, including taskable satellites, can reduce revisit times by prioritizing specific regions during emergencies. This capability is invaluable for monitoring dynamic events like floods or wildfires, where rapid response is critical.
Why Temporal Resolution and Revisit Rates Matter
Temporal resolution has emerged as a vital factor across various applications of satellite imagery. The ability to frequently capture images over the same region allows us to track environmental changes, detect natural events and manage resources effectively.
Below are key domains that rely on temporal resolution, each illustrating why revisit frequency is essential.
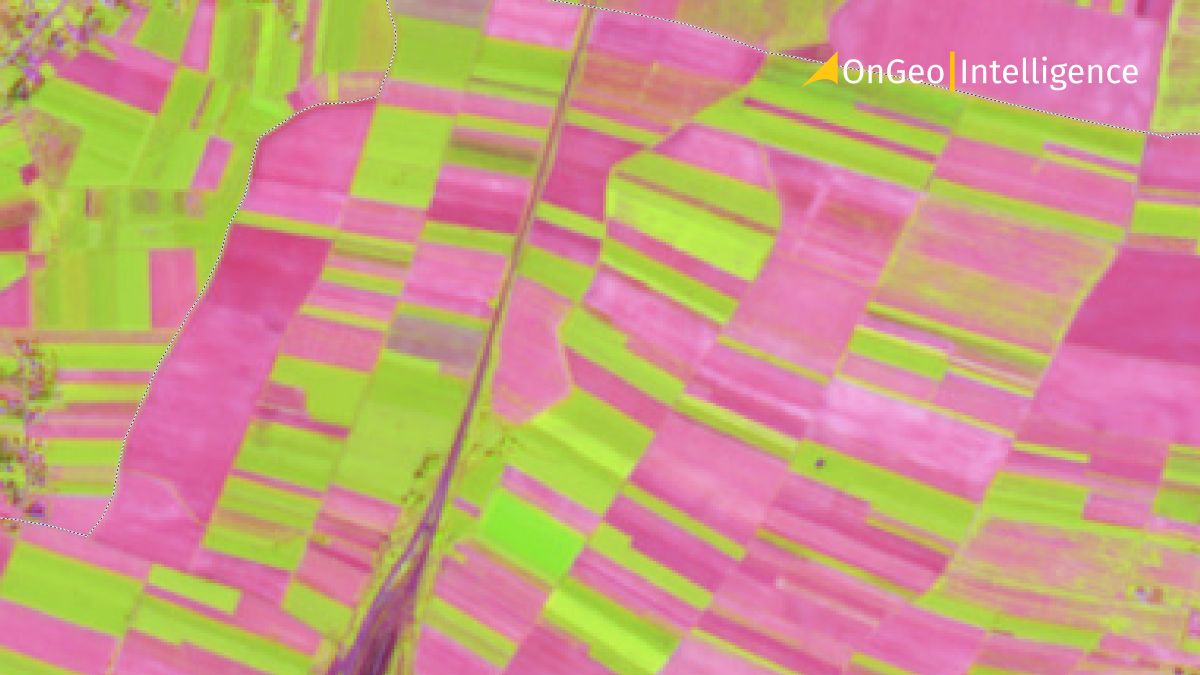
Environmental monitoring and vegetation cycles
Time-sensitive environmental processes require high temporal resolution for effective observation. Frequent revisits enable:
- Tracking vegetation growth cycles and monitoring land cover changes.
- Supporting agricultural practices by assessing crop health and optimizing harvests.
For instance, ESA's Sentinel-2 satellites, with revisit rates of 2–10 days, provide detailed vegetation indices that help agronomists make informed decisions throughout the growing season.
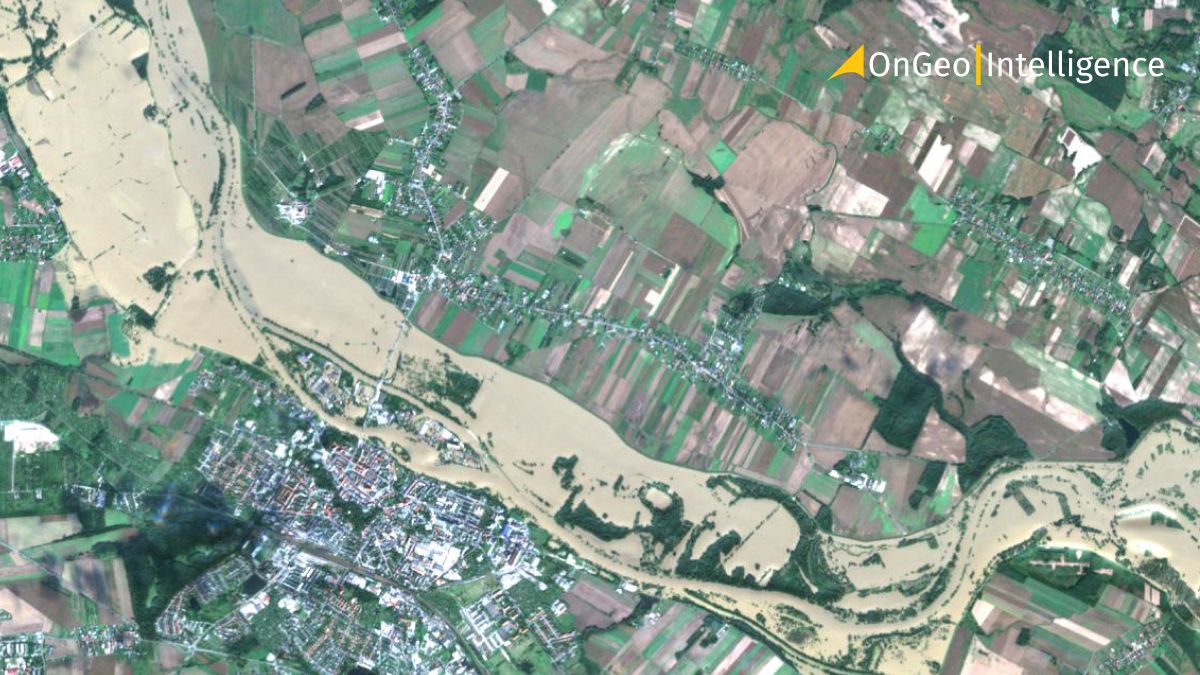
Disaster management and emergency response
In disaster scenarios, a high revisit rate is often life-saving. Natural disasters, such as hurricanes, wildfires, and floods, demand rapid and frequent data updates.
- Satellites like MODIS, with daily coverage, offer near-real-time insights for disaster tracking.
- Taskable sensors can capture affected areas on demand, significantly reducing response times.
During a flood, daily imagery reveals the extent of inundation, enabling disaster response teams to assess damage, plan evacuations, and deliver aid effectively.
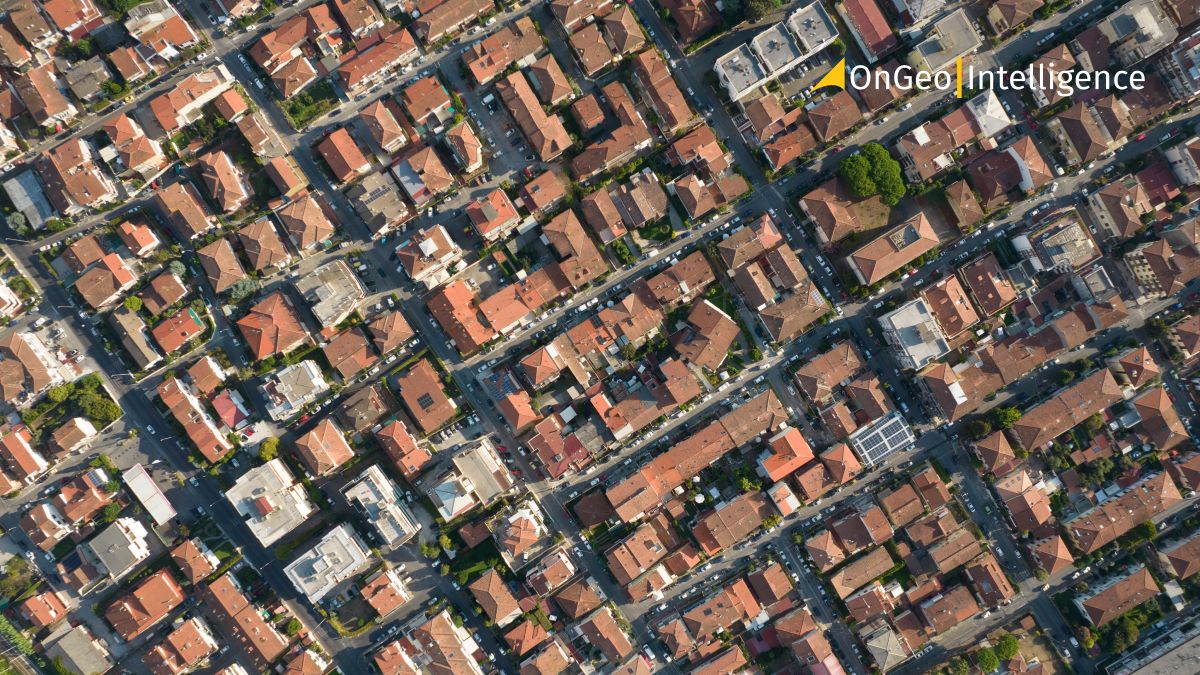
Urban development and land use changes
Urban expansion and land use changes, though gradual, benefit from consistent monitoring using moderate revisit rates. Satellites like Landsat, with revisit intervals of 8–16 days, support:
- Tracking city growth and infrastructure development.
- Monitoring deforestation and urban encroachment into rural or forested areas.
These insights are critical for sustainable urban planning and environmental impact assessments.
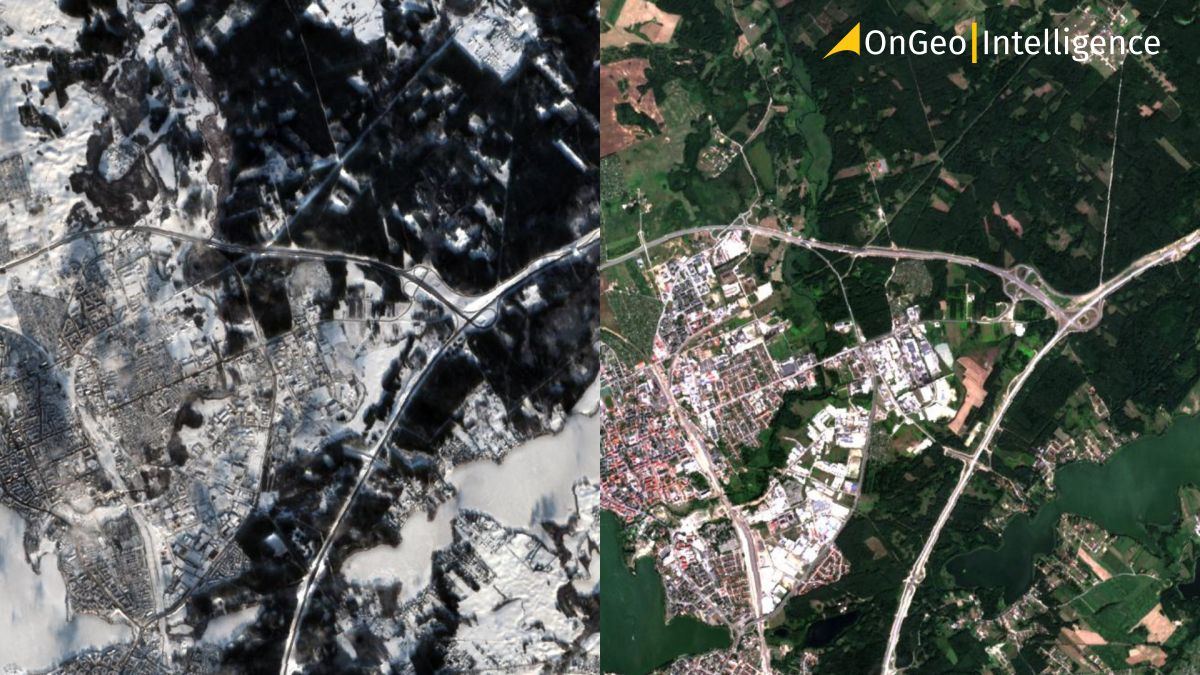
Climate change studies and long-term observations
While climate change is a long-term phenomenon, its effects often manifest in seasonal or multi-year patterns. High temporal resolution allows for:
- Monitoring polar ice melt and ocean current shifts.
- Tracking vegetation changes and ecosystem responses to global warming.
Satellites such as NASA’s MODIS provide global-scale data, enabling researchers to study these gradual yet impactful changes and refine climate models.
Technological advancements in temporal resolution
Innovations in satellite technology have significantly enhanced temporal resolution. Small satellite constellations, like Planet’s Dove fleet, now offer daily high-resolution imaging. With hundreds of satellites working in synchronized orbits, these systems deliver unmatched revisit rates, making near-continuous monitoring a reality.
Moreover, integrating satellite data with drones and ground-based sensors increases revisit frequency and enhances data accuracy. This multi-platform approach broadens the scope of Earth Observation, supporting applications ranging from precision agriculture to disaster management.
OnGeo Intelligence Satellite Imagery Report
The OnGeo-Intelligence Report leverages high-resolution imagery from a range of advanced satellites, providing reliable and accurate data for industries requiring precise asbestos monitoring solutions.
With OnGeo Intelligence, accessing satellite imagery has never been easier. The user-friendly Satellite Imagery Report offers high-quality data in a streamlined PDF format, eliminating the need for registration or long-term commitments. Users worldwide can obtain detailed imagery and actionable insights tailored to their area of interest, enabling efficient decision-making and planning across various industries. This report simplifies the process of utilizing satellite data for accurate analysis and effective strategy development.
Discover more about: OnGeo™ Intelligence Satellite Imagery Report
Conclusion
Temporal resolution and revisit rates are fundamental to effective satellite Earth Observation. From tracking dynamic environmental changes to managing urban development and responding to natural disasters, these metrics determine how quickly and accurately we can observe our planet.
As technology evolves, higher temporal resolution and shorter revisit rates will enable us to address pressing global challenges, such as climate change and sustainable resource management. By leveraging these advancements, we can make informed decisions that contribute to a better, more resilient future.