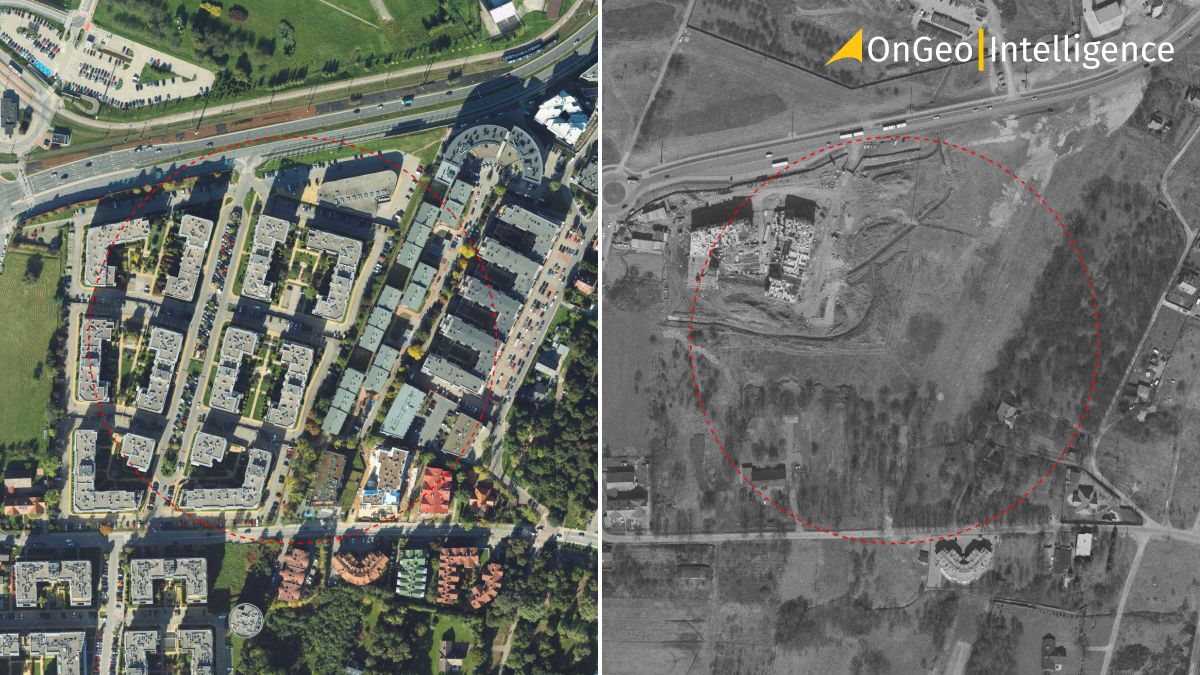
Satellite Imagery Archives: How to Access Historical Satellite Images
Satellite imagery archives are collections of Earth's images captured from space over different periods. These invaluable resources allow us to observe changes in any part of the world over the years, which is crucial for various scientific and economic fields.
OnGeo™ Intelligence Satellite Imagery Reports
OnGeo™ Intelligence offers the simplest way to obtain historical satellite images. Through the platform, you can order historical satellite images from any location on Earth for any period. The images are available in various resolutions, indicated by the size of a single pixel:
- < 1 m (very high resolution),
- 1-2 m (high resolution),
- 10 m (medium resolution, sharpened to 2.5 meters).
Generating a Report with Historical Satellite Images
Creating a report with historical satellite images on OnGeo™ Intelligence is straightforward and involves just a few steps:
Example of a Satellite Imagery Archives Report
Benefits of Using Historical Satellite Images
Historical satellite images offer several advantages, including:
- Access to historical information: They allow for the observation of changes on Earth over time, providing a valuable window into the past.
- Objective terrain view: They provide an unbiased and objective view of the terrain at a specific moment.
- Change analysis: They enable the analysis of changes in land use, land cover, topography, and other environmental aspects over time.
- Supplementing modern data: They can complement contemporary satellite data, providing a historical context and enhancing the accuracy and completeness of research findings.
- Disaster monitoring: They are helpful in assessing damage from natural disasters and planning rescue operations by providing insights into pre-disaster conditions and facilitating damage comparison.
Sources of Historical Satellite Images
There are many sources of satellite imagery archives, both free and paid. Here's a breakdown of free and paid sources for historical satellite imagery:
Free Sources of Historical Satellite Images
Free satellite imagery typically has lower spatial resolution compared to paid options, ranging from 10 to 30 meters. This means that finer details may not be visible in free satellite images from the past.
- Copernicus Open Data: Copernicus Data Space. Provides access to data from ESA's Sentinel satellites with spatial resolutions up to 10 meters, available since 2015.
- USGS EarthExplorer: EarthExplorer. A platform with access to Landsat satellite images with spatial resolutions up to 30 meters. Archive images are available from 1972.
- Google Earth/Google Maps: Google Earth / Google Maps. Offers a rich collection of historical satellite maps archives.
Paid Sources of Satellite Images
Paid sources provide historical satellite imagery of very high resolution:
- Maxar: Maxar. Formerly known as DigitalGlobe, offers a vast collection of historical satellite images with resolutions below 1 meter. For example, the WorldView-1 satellite provides images since 2007 with a resolution of 0.50 meters.
- Airbus: Airbus Earth Observation. A leading provider of historical satellite images worldwide, offering high-resolution images below 1 meter.
- Planet: Planet. Owns one of the largest fleets of small satellites, providing images with a resolution of 3-5 meters. Planet's short revisit time allows users to obtain regular updates of terrain images.
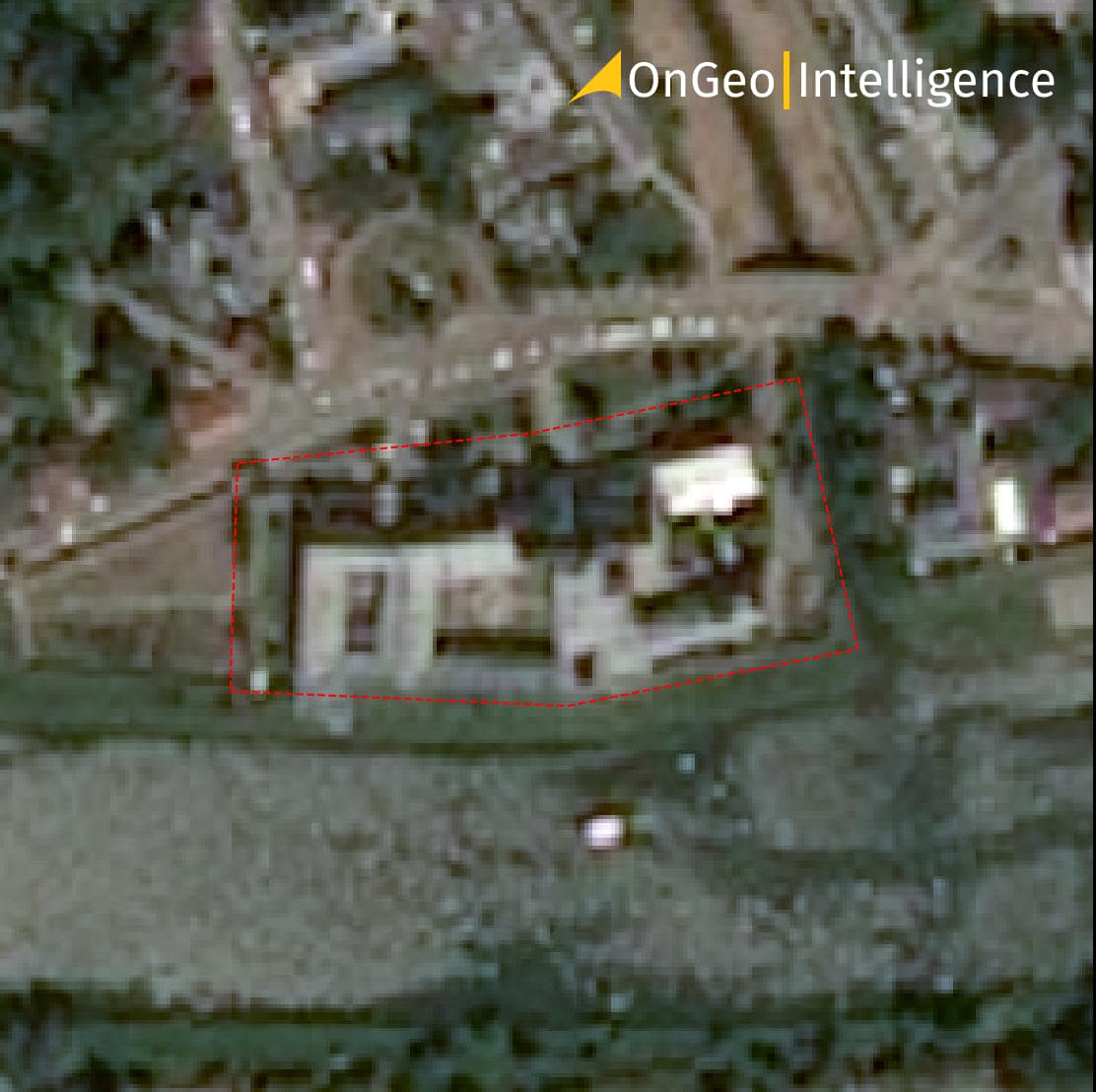
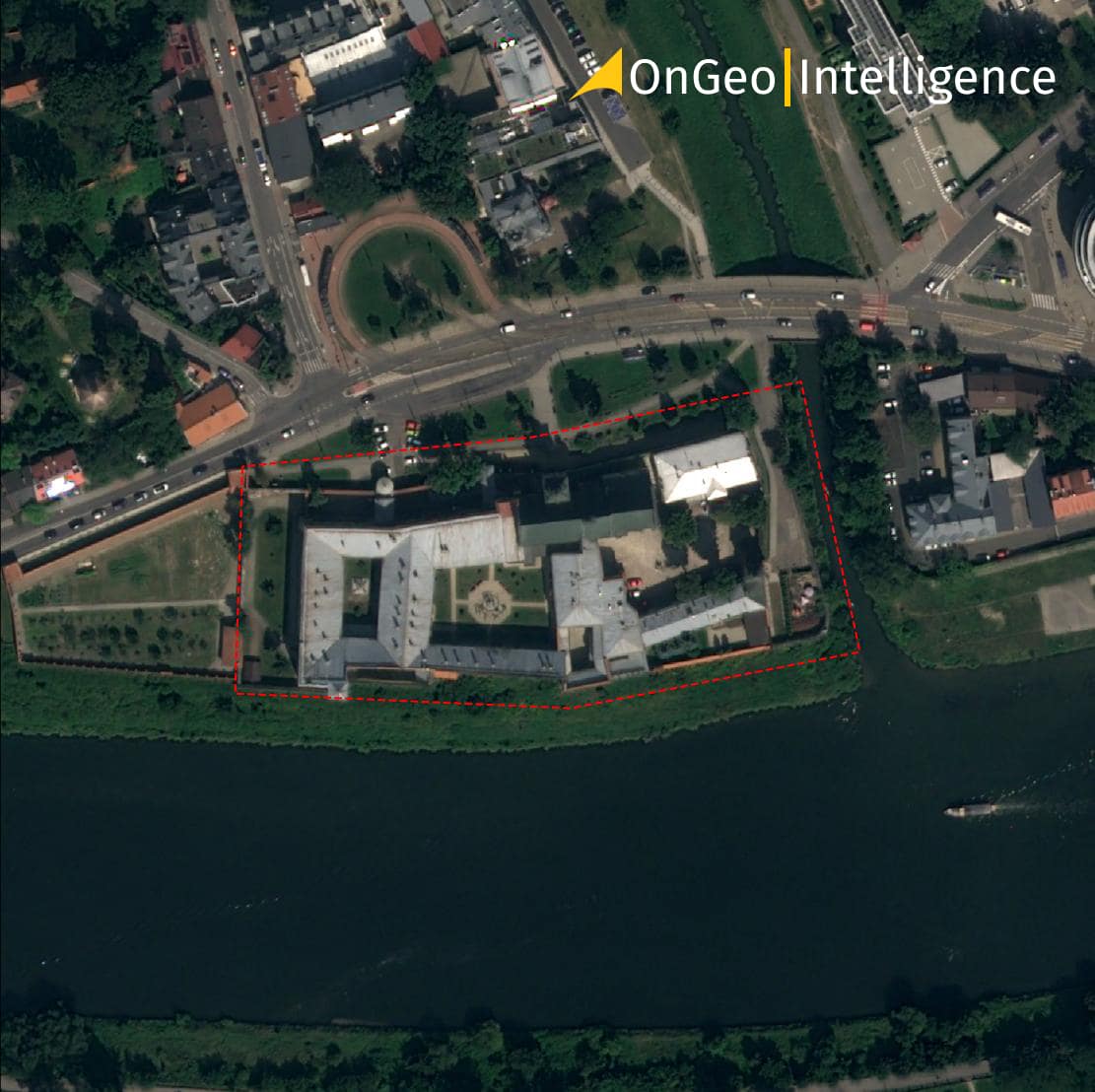

Limitations and Challenges of Using Historical Satellite Images
While historical satellite images offer a wealth of information, it's important to be aware of some limitations that can affect their usability:
Limited spatial resolution: Older satellite images, particularly those captured before the 1990s, may have significantly lower spatial resolution compared to modern imagery. This means that smaller objects and features on the ground may be difficult or impossible to distinguish. The resolution can range from tens of meters (e.g., Landsat) to hundreds of meters (e.g., early weather satellites).
Limited spectral resolution: Early satellite sensors captured data in a limited number of spectral bands compared to modern sensors. This can make it challenging to differentiate between certain land cover types or vegetation health. For example, older images may not provide detailed information about vegetation health or specific mineral compositions.
Limited availability: Data loss due to technical malfunctions, equipment damage, or limitations in early storage capabilities can result in gaps in historical archives. Additionally, political restrictions may limit access to imagery for certain regions or time periods.
Calibration and geometric correction: Historical satellite imagery may require more extensive calibration and geometric correction to account for sensor drift and variations in Earth's geometry. This can be a complex and time-consuming process for users without specialized expertise.
Mitigating the Challenges
Despite these limitations, several strategies can help users mitigate the challenges associated with historical satellite images:
Consulting with data providers: Many data providers offer detailed information about the specific limitations and characteristics of their historical imagery collections.
Combining historical with modern data: Combining historical data with high-resolution, multispectral imagery from modern satellites can provide a more complete picture and enhance the analysis.
Advanced image processing techniques: Advanced image processing techniques can be used to improve the quality and usability of historical satellite imagery, such as sharpening filters, atmospheric correction, and spectral unmixing.
Applications of Historical Satellite Images
Historical satellite images have a wide range of applications in various fields:
- Law: They can be used in courts as evidence in cases concerning property boundaries or land use changes.
- Environmental Monitoring: Historical satellite imagery plays a crucial role in environmental monitoring by allowing us to track changes in:
- Forest Cover: Monitoring deforestation rates and forest health over time.
- Glacier Retreat: Studying the decline of glaciers due to climate change.
- Land Degradation: Assessing desertification and soil erosion.
- Urban Planning and Management: Analyzing historical data helps in understanding city growth patterns, infrastructure development, and urban sprawl. This information is valuable for urban planners and policymakers.
Disaster Management: Historical satellite imagery can be used for:
Pre-disaster planning: Identifying areas prone to natural disasters like floods or landslides.
Damage assessment: Assessing the extent and severity of damage after a natural disaster.
Post-disaster reconstruction: Monitoring recovery efforts and tracking changes in affected areas.
- Archaeology and History: Old space images can be used for archaeological research in historical sites. They can help identify archaeological sites such as forts, tombs, and ancient cities.
- Climate Change Research: By analyzing trends and changes visible in historical imagery, scientists can gain insights into the long-term effects of climate change on various ecological systems.
- Reconnaissance: Old satellite images can be used to identify military objects and locate military bases, as well as detect terrain changes indicating possible military activities.
Summary
Historical satellite images have significant potential for use in modern Earth observation applications. They can provide valuable information about the natural environment, climate change, topography, and many other aspects. Their ability to facilitate comparison and change analysis over time makes them invaluable for various scientific studies.
However, the use of historical satellite images also has limitations and challenges, such as low spatial resolution and limited archive availability. To maximize their value, it is essential to select appropriate images for specific applications, conduct necessary data processing and analysis, and consider potential limitations.
Despite these challenges, historical satellite images remain a valuable resource for scientific and applied tasks in remote sensing. They can complement contemporary data, increasing the accuracy and completeness of research findings. By understanding their strengths and limitations, researchers can leverage historical satellite imagery to gain valuable insights into our planet's past, present, and future.
Related articles
- Real-Time Satellite Imagery
- Satellite Imagery Report - generate it yourself
- What Is Location Intelligence? A Guide for Modern Businesses
- High Resolution Satellite Imagery: Best Quality Sources
- Satellite Maps: Viewing Your Neighborhood and Beyond
- Satellite Image Resolution
- Airbus Satellite Imagery for Earth Observation
- Pansharpening: The Secret to Sharper, More Detailed Satellite Images
- CORONA Satellite Imagery: The Spy Satellites History