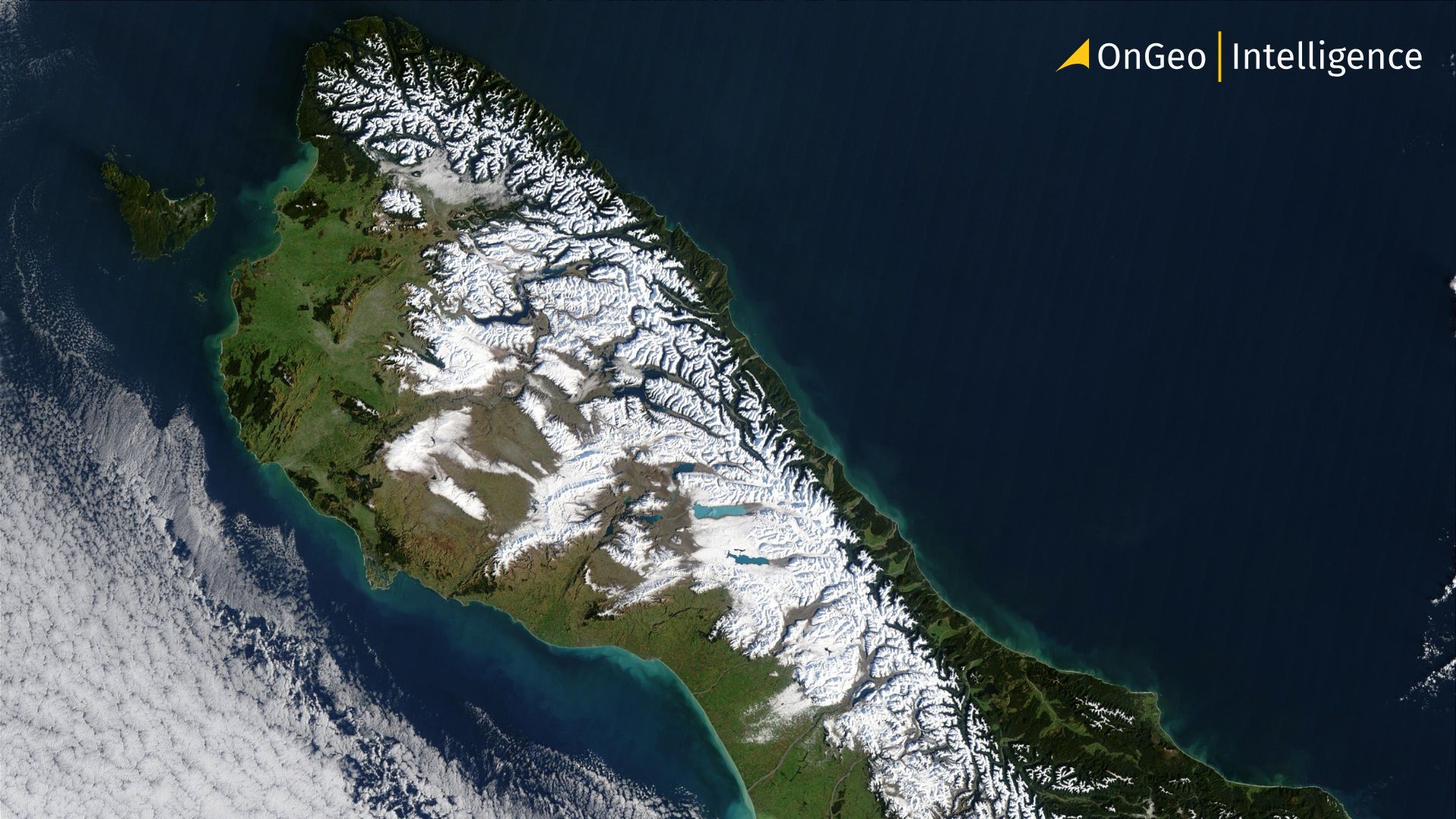

Orthorectification: The Hidden Hero of Satellite Imagery in GIS
Satellite and aerial imagery play a vital role in modern mapping and geospatial analysis. But to unlock their full potential in GIS applications, a critical preprocessing step is needed – orthorectification. This process ensures imagery can be trusted for real-world measurements, making it a cornerstone of Earth Observation workflows.
Understanding Orthorectification
Orthorectification is the transformation of raw satellite or aerial images into geometrically corrected data that accurately represents the Earth's surface. Raw imagery is often distorted due to terrain elevation, camera tilt and sensor geometry. These factors result in a warped image where distances, angles or positions cannot be reliably measured. Orthorectification corrects these distortions, adjusting each pixel as if it were captured directly from above – at the sensor’s nadir point. The result is an image with uniform scale and precise geolocation, known as an orthophoto or orthoimage.
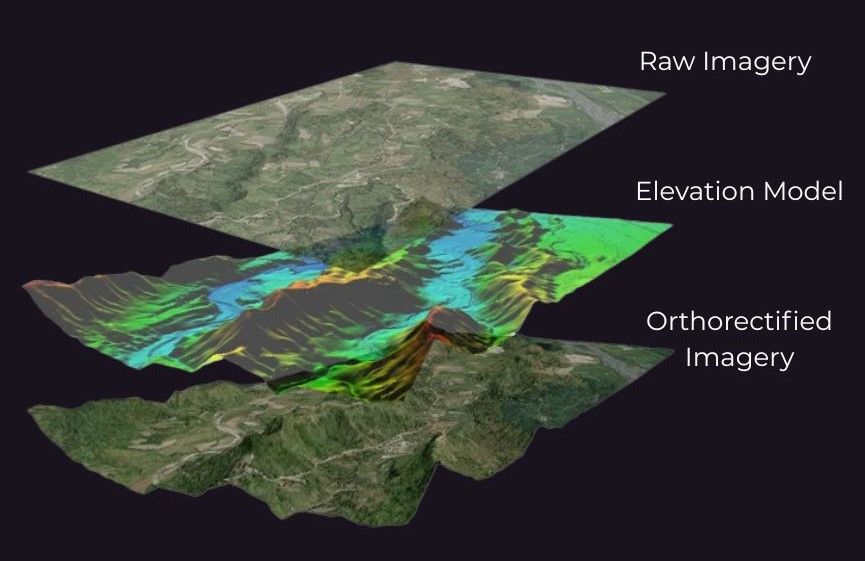
The Importance of Orthorectification
Why is this important? Simply put, without orthorectification, satellite images cannot be used for accurate mapping or analysis. Distorted imagery may cause objects to appear in the wrong place, lean at unnatural angles or overlap with surrounding features. This is especially problematic in areas with significant terrain variation or dense urban environments. Orthorectification solves this by aligning imagery with real-world coordinates and eliminating the visual inconsistencies caused by relief displacement.
Orthorectified Imagery in GIS Applications
One of the greatest benefits of orthorectified imagery is its usability in Geographic Information Systems (GIS). These corrected images can be integrated with vector data, used for change detection or serve as basemaps in applications ranging from urban planning to disaster response. Unlike traditional maps that rely on symbolic representation, orthophotos provide realistic visual context while maintaining cartographic precision. They allow users to measure true ground distances and areas, making them ideal for land surveying, infrastructure design or environmental monitoring.
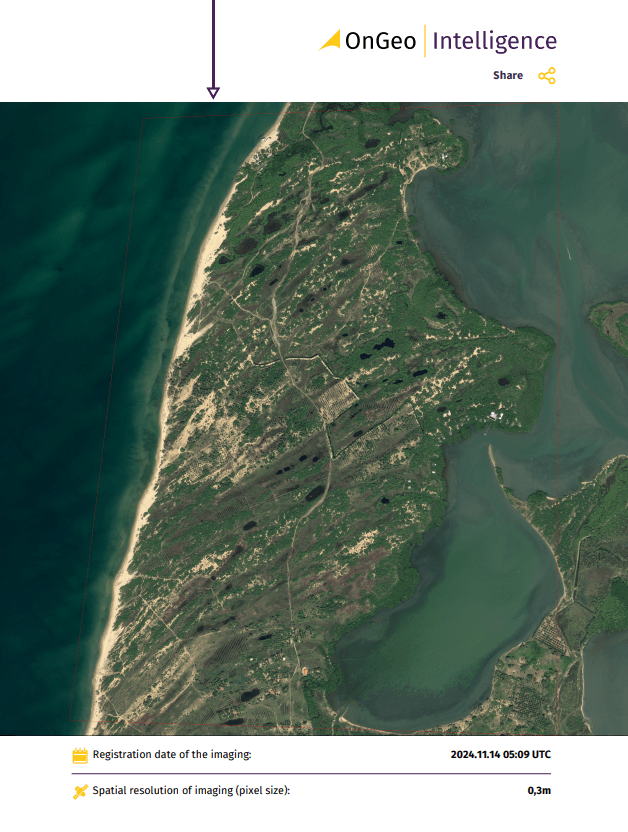

OnGeo Intelligence Satellite Image Report
The service provides detailed satellite images tailored to the user’s selected area and time period. This comprehensive report includes a chronological arrangement of satellite imagery, offering clear insights into changes over time. Requested data will be delivered in a PDF document and georeferenced Sentinel-2 data. Users can choose from a range of image resolutions to meet their specific needs, including:
- very high-resolution images: 0.3 - 1.0 meters,
- high-resolution images: 1-2 meters,
- images with a 10-meter resolution.
Enjoy exceptional convenience and accessibility with the OnGeo Intelligence Satellite Imagery Report service – no account registration, contracts, or subscription fees required.
Diverse Applications of Orthorectified Imagery
Applications of orthorectified imagery are vast and growing. In forestry, orthoimages help track deforestation and vegetation health. In coastal areas, they support shoreline mapping and erosion monitoring. Urban planners use them to map land use changes and assess building footprints over time. In emergency management, orthorectified satellite data provides fast and accurate visuals of flood zones, wildfires or earthquake damage. Even in the detection of hazardous materials, such as asbestos roofing, orthorectified imagery combined with remote sensing techniques has proven highly effective.
Key Steps in the Orthorectification Process
The orthorectification process involves several critical steps to ensure the accuracy of the final orthoimage. These include:
Data Collection: Acquiring raw satellite or aerial imagery along with metadata such as sensor position and orientation.
Terrain Modeling: Using Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) to account for terrain variations and correct relief displacement.
Geometric Correction: Adjusting pixel positions to align with real-world coordinates, compensating for camera tilt and sensor distortions.
Resampling: Applying interpolation techniques to create a uniform scale and seamless image output.
Quality Control: Verifying the accuracy of the orthophoto against ground control points to ensure precise geolocation.
The Critical Role of Orthorectification in Geospatial Intelligence
In summary, orthorectification may not be visible to most users but it plays a critical role behind the scenes in turning raw satellite data into actionable geospatial intelligence. It ensures accuracy, consistency and reliability – qualities essential for informed decision-making across countless sectors. As demand for high-resolution imagery grows, orthorectification remains a foundational process in satellite Earth Observation and the broader GIS ecosystem.